Understanding the difference between AC and DC is important for solar energy. For photovoltaic technology to be used in our businesses, offices, and industrial areas it must be converted from direct (DC) to alternating current. Depending on the system and application, it may be better to use DC directly instead of converting to an AC source. This blog discusses the pros and cons of using AC solar panels between AC and DC and how solar AC systems compare to their DC counterparts.
Differentiate AC & DC Power
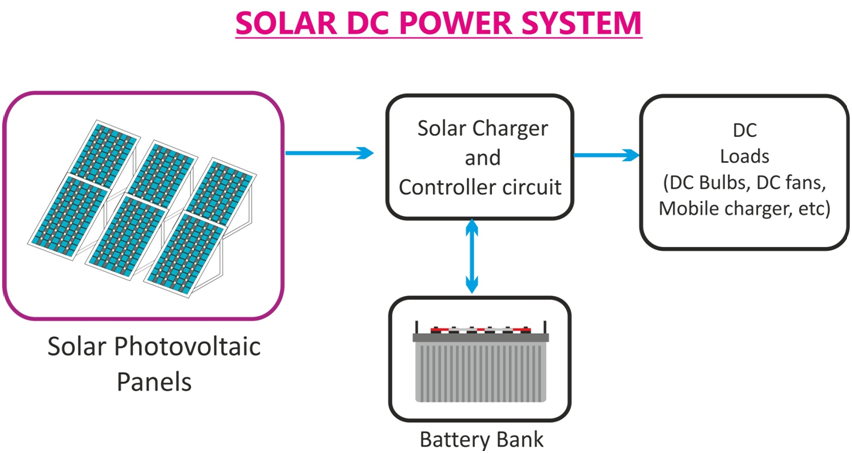
When it comes to solar electricity, it is important to understand the difference between alternating and direct currents. Photovoltaic technology works with direct current, which means that the power coming from the solar panel is pure direct current. However, this unregulated DC power supply cannot be used directly for utility applications. So some electronic circuit is needed to convert the current source into usable energy, whether direct or alternating.
The decision to use direct current or alternating current in photovoltaic systems is a challenging one. Both options may be better depending on the AC or DC system type and application. It is important to remember that the general power supply of our industries, offices, etc., runs on AC, and most of the appliances, electrical appliances, lights, fans, etc., in the market run on ac solar systems.
In a DC system, the system has the advantage of avoiding DC-AC conversion losses. It also reduces the cost of any inverter circuits or reverses technology. However, DC-based systems can only operate on lower standard DC voltages such as 6v, 12v, 2v, and 8v.
AC systems require an additional inverter circuit to convert direct current into a usable single or three-phase AC source.
Advantages of DC in Solar:
- Simplicity: DC solar panels are easier to install, operate, and maintain than AC solar panels, making them a more user-friendly choice for small commercial solar applications.
- Safety: DC voltage is generally considered safer than AC voltage since it does not produce electric shock or electrocution in case of accidental contact.
- Battery compatibility: DC solar panels are more easily compatible with battery storage systems, which are increasingly used to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during peak demand times.
Disadvantages of DC in Solar:
- Limited distance: DC voltage has a limited distance that it can travel before it experiences a significant voltage drop, which can reduce efficiency.
- Incompatibility with the grid: DC solar panels are not directly compatible with the AC grid, requiring additional equipment to be connected.
- DC to AC conversion: To use DC solar power in AC appliances, it must be converted through an inverter, which can be costly and reduce overall efficiency.
Advantages of AC in Solar:
- Long-distance transmission: AC voltage is better suited for long-distance electricity transmission since it experiences less voltage drop over distance.
- Grid compatibility: AC solar panels are directly compatible with the AC grid, so they can be easily connected to the existing grid infrastructure.
- Higher voltage: AC voltage can be easily stepped up or down, making transmitting power at high voltages easier, and reducing energy losses during transmission.
Disadvantages of AC in Solar:
- Less efficient: AC solar panels are generally less efficient than DC solar panels since they require a conversion from DC to AC, which results in energy loss.
- Higher cost: AC solar panels are often more expensive than DC solar panels, making them less cost-effective for smaller installations.
- Complexity: AC solar panels require additional equipment for conversion, which makes them more complex to install, operate, and maintain.
The two types of Solar AC power systems are:
1. Battery-powered or hybrid solar energy systems
In battery-powered or hybrid solar energy systems, solar energy is converted into an AC source using an inverter. The inverter can also charge a battery bank as a data carrier. The battery bank can then be used as a power source when there is no sunlight or the solar panels are not producing enough energy.
These systems are particularly useful when the power grid is unreliable or unavailable, and a backup power source is required. They are also useful for industrialists who want to maximize their solar electricity consumption.
2. Grid and batteryless systems
Grid and batteryless solar systems convert all solar energy directly into AC and have no battery. These systems are connected to the grid, and the excess electricity produced by the solar panels is fed back into the grid. These systems are mainly used where the network supply is reliable, and the price of electricity is high.
On-grid and battery-free systems are also known as grid-tied systems and are the most common solar systems used in commercial applications.
LED lights, smaller fans, and similar products are usually available on DC power. Still, many common appliances such as air conditioners and refrigerators that require more power are not available on the market that are suitable for DC power. In systems that require the operation of such larger equipment, solar energy systems are not an option, and solar energy systems are necessary.
In DC systems, the rated current increases very quickly in the higher power classes due to the lower voltage. For example, a 10,000W solar power system running on a 12V DC bus has a rated output of 834 amps.
This increase in current ratings makes managing such a large current rating very difficult and expensive. It also adds cables, a switch, and other costs that may not outweigh the smaller benefits.
Also, DC cables are more expensive than AC cables of the same size. Therefore, as a rule, DC power systems can be suitable for lower power or applications where the power defaults to DC, such as LED lights, DC fans, telecommunications systems, cathodic protection systems, etc. Solar energy systems are more relevant, reliable, and cost-effective for a higher power.
The choice between an AC or DC solar system depends on the application’s specific requirements. A solar power system is more suitable for low-power equipment and remote locations. Higher power needs and more complex applications require a solar energy system. Consulting with a qualified solar installer is always recommended to determine the best solar system for your specific needs.
Final Thoughts
Different scenarios require the use of either DC or AC in solar systems. DC systems are generally more reliable and efficient when using solar energy for basic electricity needs. However, for larger applications such as grid-tied systems, AC is the better option due to its higher power output and compatibility with other renewable energy sources. Ultimately, the best choice depends on the individual’s needs and preferences.
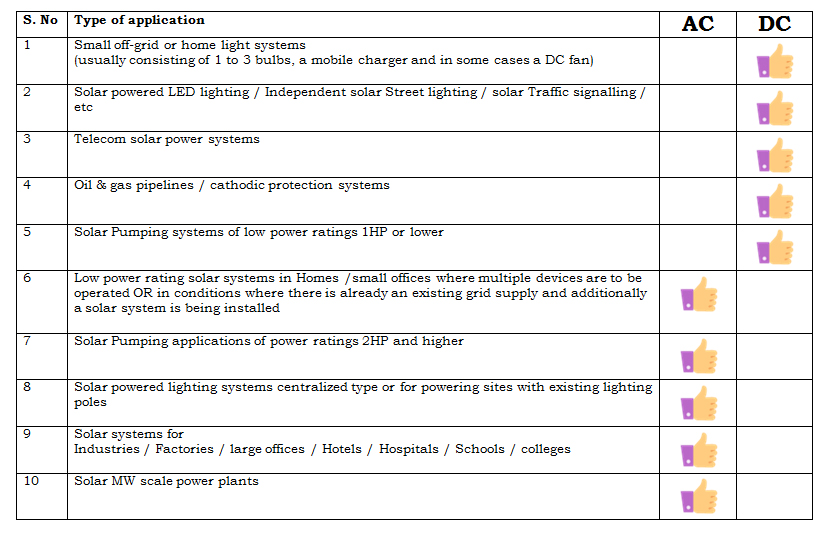
Here below is the table provided, along with recommendations for the best solar inverter technologies:
Check out solar Panels: A Brief Guide on selecting the right one

