MPPT technology has become very popular in solar electronics and is, in fact, the de-facto standard for on-grid / string inverters.
MPPT stands for Maximum Power Point Tracking.
MPPT is basically an algorithm and implemented through a combination of software and electronics hardware in any inverter or solar controller.
It helps in ensuring that the output from the solar panel or array or solar string is at it’s peak / maximum. This is done by a continuous power tracking methodology so as to settle at the most optimal power point from the solar panels.
The Maximum power of a solar module varies with solar radiation, ambient temperature and cell temperature. Solar cells have a complex relationship between temperature and total resistance that produces a non-linear output efficiency based on the I-V curve. The objective of MPPT system is to sample the output of the PV modules and apply the proper resistance to obtain maximum power for any given solar radiation and overall environmental conditions.
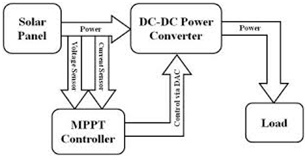
How is MPPT applied in solar circuits
When a load is directly connected to the solar panel, the operating point of the panel will rarely be at peak power. The impedance seen by the panel derives the operating point of the solar panel. Thus by varying the impedance seen by the panel, the operating point can be moved towards peak power point. Since panels are DC devices, DC-DC converters must be utilized to transform the impedance of one circuit (source) to the other circuit (load). Changing the duty ratio of the DC-DC converter results in an impedance change as seen by the panel. At a particular impedance (or duty ratio) the operating point will be at the peak power transfer point. The I-V curve of the panel can vary considerably with variation in atmospheric conditions such as radiance and temperature. Therefore it is not feasible to fix the duty ratio with such dynamically changing operating conditions.
MPPT implementations utilize algorithms that frequently sample panel voltages and currents, then adjust the duty ratio as needed. Microcontrollers are employed to implement the algorithms.
On the hardware side MPPT technology is implemented by use of DC-DC conversion technology with high switching frequencies typically in the range of 15 to 80 KHz. Such high switching frequency has the advantage of being more efficient. But it also brings the challenges of EMI, etc. To achieve the best result and optimum ratio of Efficiency, performance and reliability requires a very careful design.
There is also a software and microcontroller to control the whole process and continuously seek the most optimal solar array power point. On this front there are various methods to achieve MPPT technology . Some of the commonly used ones are :
- Perturb and Observe
- Incremental Conductance
- Current Sweep
- Constant voltage
A practical Example
- single solar Module
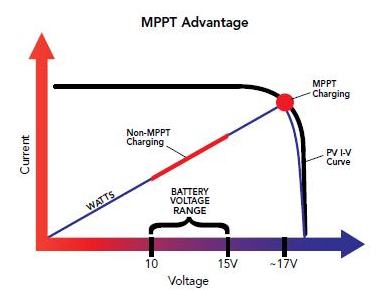
A PV module is a constant current type device. As shown on a typical PV module voltage vs. current curve, current remains relatively constant over a wide range of voltage. A typical 75 watt module is specified to deliver 4.45 amps @ 17 volts @ 25 C cell temperature. Conventional PV controllers essentially connect the PV array directly to the battery when battery is discharged. When a 75 watt module is connected directly to a battery charging at 12 volts, the module still provides approximately the same current. But, because output voltage is now at 12 volts rather than 17 volts, module power production is artificially limited and the 75W module only delivers 53 watts. This wastes 22 watts of available power.
Solar charger controller’s MPPT technology operates in a very different fashion. Under these conditions Solar charger controller calculates the maximum power voltage (V) at which the PV module delivers maximum power, in this case 17 volts. It then MPPT operates the module 17 volts which extracts maximum available power from the module. Solar charger controller continually recalculates the maximum power voltage as operating conditions change. Input power from the maximum power tracking controller, in this case 75 watts, feeds a switching type power converter which reduces the 17 volt input to battery voltage at the output. The full 75 watts which is now being delivered at 12 volts would produce a current of 6.25 amps. A charge current increase of 1.8 amps or 40% is achieved by converting the 22 watts that would have been wasted into useable charge current. Note that this example assumes 100% efficiency to illustrate the principal of operation. In actual operation, boost will be somewhat less.
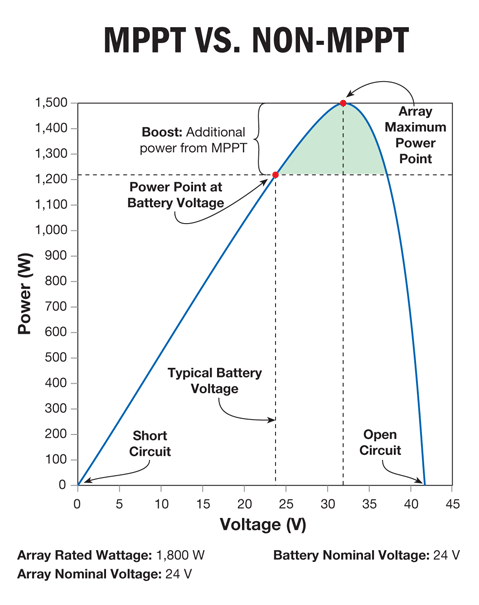
- Solar array comparision
Considering the case of an array with STC rated power of 1800w. Given below is a chart showing the comparision in such a scenario.
Conclusion
Hence, from the above it becomes very apparent that MPPT technology helps in generating maximum power from the solar modules / solar array. In fact that is the reason that MPPT technology is today the common standard in all kinds of solar grid-tie inverters and also the standard for larger battery based inverters.
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]